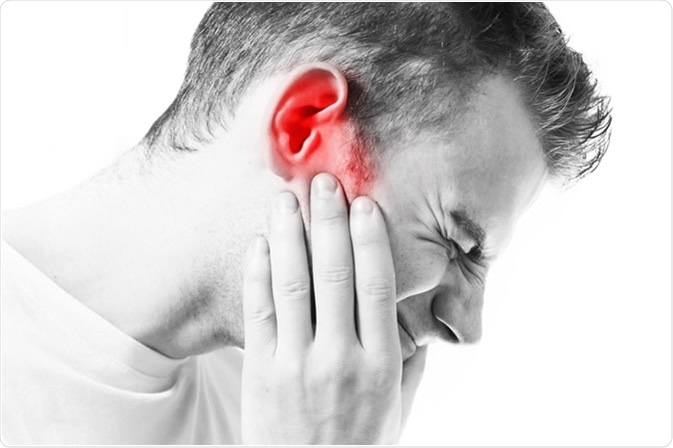
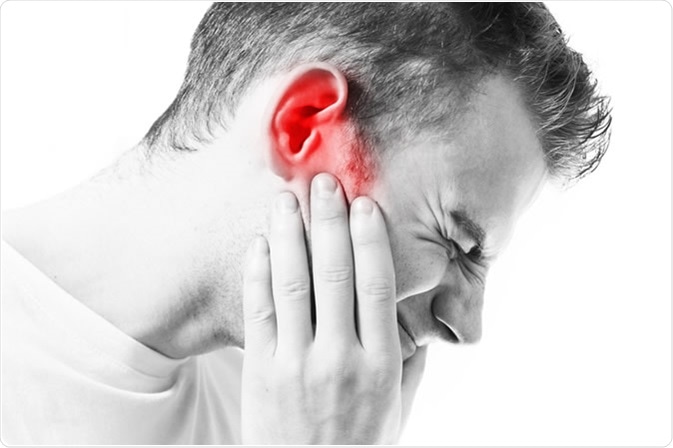
What is Tinnitus?
Experiencing ringing or other noises in one or both of your ears it is called Tinnitus. The noise you hear when you experience tinnitus is not caused by an external sound, and other people usually cannot hear it. Tinnitus is a typical problem. It affects about 20% of people, and is particularly common in older adults.
Mainly, an underlying condition can become the cause of tinnitus, for example, an ear injury or a problem with the circulatory system and age-related hearing loss. For most of the people, tinnitus gets better with treatment of the latent cause or with other treatments that mask or diminish the noise, making tinnitus less noticeable.
Check out top 10 noise isolating earbuds in 2021.
What are the symptoms?
Even though no external sound is present, tinnitus is most frequently described as a ringing in the ears. Other types of phantom noises in your ears, such as, buzzing, roaring, humming, clicking, hissing can be triggered by tinnitus.
Most people who experience tinnitus have mostly subjective tinnitus, or tinnitus that only you can hear. The noises of tinnitus may differ in pitch from a a high squeal to a low roar, and you may hear it in one or both ears. In some occasions, the sound can be so loud that it might interfere with your ability to concentrate or hear external sound. Tinnitus may come and go or be present all the time.
Rarely, tinnitus can start as a whooshing sound or a rhythmic pulsing, frequently in time with your heartbeat (it is called pulsatile tinnitus). Your doctor may be able to hear your tinnitus when he/she does an examination, if you have pulsatile tinnitus (it is called objective tinnitus).
What are the risk factors?
Any person can experience tinnitus, but following factors may increase your risk:
1) Loud noise exposure – Loud noises, such as those from chain saws, heavy equipment and firearms, are typical sources of noise-related hearing loss. If played loudly for long periods, portable music devices, like MP3 players, also can cause noise-induced hearing loss. People who work in noisy environments, for instance, construction and factory workers, soldiers and musicians are particularly at risk
2) Elderliness – As you get older, the number of functioning nerve fibers in your ears diminishes, possibly causing hearing problems frequently related to tinnitus
3) Sex – Men are more likely to experience tinnitus
4) Tobacco and alcohol use – Smokers have a higher risk of developing tinnitus. Drinking alcohol also grows the risk of tinnitus
5) Specific health problems – Cardiovascular problems, obesity, high blood pressure, and a history of head injury or arthritis all grow your risk of tinnitus.
Click here to find out about different types of earbuds and more.
How to prevent?
In majority of cases, tinnitus is the consequence of something that can’t be avoided. Although, some precautions can help prevent specific kinds of tinnitus.
1) Utilize hearing protection – Exposure to loud sounds can harm the nerves in the ears, causing hearing loss and tinnitus. Try to restrain your exposure to very loud sounds. At least, use ear protection to help protect your hearing, if you cannot avoid loud sound. If you are a musician, work in an industry that utilizes loud machinery, use chain saws or use firearms, especially shotguns or pistols, make sure to always wear hearing protection.
2) Turn down the volume – Listening to music at very high volume through headphones or long-term exposure to amplified music with no ear protection can become a reason of tinnitus and hearing loss.
3) Take care of your cardiovascular health – Eating right, regular exercise and taking further steps to maintain your blood vessels healthy can help avoid tinnitus linked to blood vessel disorders and obesity.
4) Limit caffeine, alcohol and nicotine – These substances, can affect blood flow and contribute to tinnitus, especially when used in excess.